Nutritional Composition of Apple Cider Vinegar
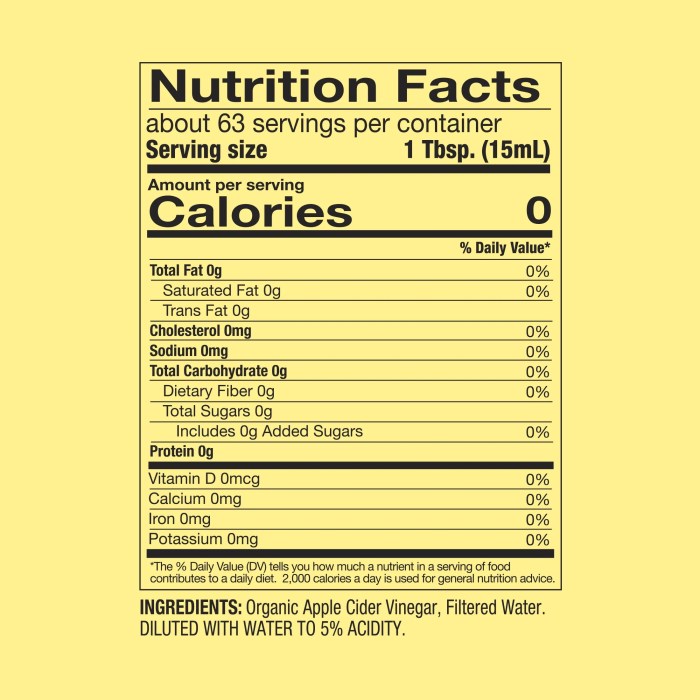
Apple cider vinegar nutrition facts – Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is a fermented product derived from apples, and while it’s primarily known for its purported health benefits, it does offer a small amount of nutrients. Its nutritional profile is relatively modest, but understanding its composition is crucial for assessing its role in a balanced diet. It’s important to note that the nutritional content can vary depending on the brand and production methods.
Macronutrient Composition of Apple Cider Vinegar
The macronutrient content of apple cider vinegar is low. It’s primarily composed of water and contains negligible amounts of carbohydrates, protein, and fat. The following table provides a general overview of the macronutrient content per serving (typically one tablespoon, approximately 15ml). Note that these values can fluctuate slightly depending on the specific product.
| Nutrient | Amount per serving (1 tablespoon) | Unit | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 0-1 | grams | <1% |
| Protein | 0 | grams | 0% |
| Fat | 0 | grams | 0% |
Micronutrients in Apple Cider Vinegar
While not a significant source of vitamins and minerals, apple cider vinegar does contain trace amounts of several micronutrients. These are largely retained from the original apples and the fermentation process. The concentrations are generally low, and it shouldn’t be relied upon as a primary source of these nutrients.
The following micronutrients may be present in varying amounts:
- Potassium: Contributes to maintaining healthy blood pressure and muscle function.
- Acetic Acid: The main component of ACV, with various potential health effects (discussed below).
- Small amounts of other vitamins and minerals: These may include trace amounts of vitamin C, B vitamins, and minerals like magnesium and calcium, though the quantities are minimal.
Acetic Acid and its Role, Apple cider vinegar nutrition facts
Acetic acid is the primary bioactive compound in apple cider vinegar, responsible for its characteristic sour taste. It’s formed during the fermentation process of apples. Many of the purported health benefits associated with apple cider vinegar are attributed to acetic acid. Research suggests potential roles in blood sugar control, improved insulin sensitivity, and aiding weight management, although more research is needed to confirm these effects definitively.
It’s important to note that these benefits are usually associated with moderate consumption and shouldn’t replace medical advice or treatment.
Health Benefits Associated with Apple Cider Vinegar Consumption: Apple Cider Vinegar Nutrition Facts

Apple cider vinegar (ACV), a fermented product derived from apples, has gained popularity for its purported health benefits. While more research is needed to definitively confirm many of these claims, several studies suggest potential positive effects on various aspects of health. This section will explore some of the key health benefits associated with ACV consumption, focusing on areas supported by existing scientific evidence.
Blood Sugar Control and Weight Management
Several studies suggest that ACV may play a role in blood sugar control and weight management. The acetic acid in ACV is believed to be a key component in these effects. It’s thought to improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body more effectively utilize glucose. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
One study published in the
Journal of Functional Foods* found that consuming ACV before a high-carbohydrate meal led to a significant reduction in postprandial blood glucose levels.
“Consumption of vinegar before a high-carbohydrate meal lowered postprandial blood glucose levels and improved insulin sensitivity in subjects with type 2 diabetes.”
Apple cider vinegar boasts various nutritional benefits, though it’s low in calories and macronutrients. Its health advantages often stem from its acetic acid content. For a contrasting example of a nutrient-rich food, you might compare it to the impressive array of vitamins and minerals found in seaweed salad nutrition facts , which offer a different nutritional profile altogether.
Ultimately, both apple cider vinegar and seaweed salad contribute to a balanced diet in their own ways.
Regarding weight management, some research suggests that ACV may promote feelings of fullness, potentially leading to reduced calorie intake. This effect is likely due to ACV’s impact on satiety hormones. However, it’s crucial to remember that ACV is not a magic weight-loss solution; its effects are modest and should be considered as part of a holistic approach to weight management that includes a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Impact on Gut Health and the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome, the complex community of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, plays a vital role in overall health. Emerging research indicates that ACV may exert beneficial effects on the gut microbiome composition and function. The acetic acid in ACV possesses antimicrobial properties, potentially inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria while promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria.
This balanced microbial environment can contribute to improved digestion, enhanced nutrient absorption, and a strengthened immune system. While the specific mechanisms are still being investigated, the potential for ACV to positively influence gut health is a promising area of ongoing research. Further studies are needed to fully elucidate the complex interactions between ACV and the gut microbiome.
Comparison of Nutritional Benefits with Other Vinegars
While apple cider vinegar is often highlighted for its potential health benefits, it’s important to consider how it compares to other types of vinegar. The nutritional composition varies across different vinegars, impacting their respective health benefits.
| Vinegar Type | Key Nutrient | Amount (per tablespoon) | Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple Cider Vinegar | Acetic Acid | ~1 gram | Blood sugar control, potential weight management support, gut health |
| White Vinegar | Acetic Acid | ~1 gram | Similar to ACV, but with less potential additional nutrients |
| Red Wine Vinegar | Acetic Acid, antioxidants | ~1 gram, variable antioxidant content | Blood sugar control, potential antioxidant benefits |
| Balsamic Vinegar | Acetic Acid, antioxidants, polyphenols | ~1 gram, variable antioxidant and polyphenol content | Blood sugar control, potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits |
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Apple Cider Vinegar

While apple cider vinegar offers potential health benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of its potential drawbacks. Consuming it improperly or in excessive amounts can lead to several adverse effects, highlighting the importance of moderation and informed usage. This section will detail these risks and offer guidance on safe consumption practices.
The acidic nature of apple cider vinegar is the primary source of its potential risks. This acidity can cause damage to tooth enamel with prolonged exposure, leading to increased sensitivity and potential cavities. Furthermore, apple cider vinegar can interact negatively with certain medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or causing unwanted side effects. Individual sensitivities also play a role, with some people experiencing digestive upset or allergic reactions.
Tooth Enamel Erosion
The high acidity of apple cider vinegar can erode tooth enamel over time. Regular and prolonged exposure, especially without proper rinsing, can weaken teeth and make them more susceptible to decay. The effect is similar to that of other acidic beverages, but the concentrated nature of apple cider vinegar can exacerbate the problem. To mitigate this risk, it’s recommended to dilute apple cider vinegar significantly before consumption and to rinse the mouth thoroughly with water afterward.
Consider using a straw to minimize contact with teeth.
Interactions with Medications
Apple cider vinegar can interact with certain medications, particularly those affecting blood sugar levels (like insulin or diabetes medications) or potassium levels. Its ability to lower blood sugar can lead to hypoglycemia if taken alongside such medications. Similarly, its impact on potassium levels could exacerbate issues for individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions or those on medications affecting potassium balance.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating apple cider vinegar into your diet if you are taking any medications.
Recommended Daily Intake and Consequences of Exceeding It
There’s no universally agreed-upon recommended daily intake of apple cider vinegar, as individual tolerance varies significantly. However, starting with small amounts (e.g., 1-2 tablespoons diluted in water) and gradually increasing the intake while monitoring for any adverse effects is a prudent approach. Exceeding recommended limits can lead to several negative consequences.
It is important to note that exceeding the recommended intake of apple cider vinegar can have detrimental effects on your health. The following list details some potential negative consequences:
- Severe tooth enamel erosion leading to sensitivity and cavities.
- Gastrointestinal distress, including heartburn, nausea, and stomach upset.
- Low blood potassium levels (hypokalemia), potentially causing muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart problems.
- Interactions with medications, leading to reduced effectiveness or adverse reactions.
- Esophageal erosion, particularly in individuals with pre-existing esophageal conditions.
FAQ Resource
Is apple cider vinegar a good source of calories?
No, apple cider vinegar is very low in calories.
Can I drink apple cider vinegar undiluted?
It’s generally recommended to dilute apple cider vinegar with water before consumption to minimize the risk of tooth enamel erosion and potential digestive upset.
Does apple cider vinegar interact with any medications?
Yes, apple cider vinegar can interact with certain medications, particularly those affecting blood sugar levels. Consult your doctor if you are on medication.
What are the best ways to incorporate apple cider vinegar into my diet?
Apple cider vinegar can be added to salad dressings, marinades, soups, or simply diluted in water as a beverage. Many people also enjoy it in smoothies.
Is apple cider vinegar effective for weight loss?
While some studies suggest a potential link between apple cider vinegar and weight management, more research is needed to confirm its efficacy. It is not a miracle weight loss solution.
